The tangential flow filtration market refers to the range of products and technologies used for the separation and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, DNA, and viruses. This technique is used in a variety of applications including biopharmaceutical production, research and development, and laboratory testing. The market for tangential flow filtration is expected to grow due to the increasing demand for biopharmaceuticals, the need for high-quality and pure products, and the growing adoption of single-use technologies in biopharmaceutical production.
Get Sample PDF Report with Graphs and Figures Here
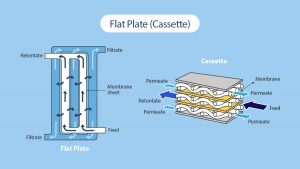
Tangential flow filtration (TFF) is a separation technique that utilizes a semi-permeable membrane to separate and purify biomolecules such as proteins, DNA, and viruses from a solution. In TFF, the solution flows tangentially along the surface of the membrane, allowing for the separation of the desired molecules based on their size and molecular weight. The permeate, or purified solution, passes through the membrane, while the retentate, or concentrated solution, is recirculated. TFF is used in a variety of applications, including biopharmaceutical production, research and development, and laboratory testing. TFF systems typically consist of a filtration unit, a pump, and a control unit.
Normal flow filtration (NFF) and tangential flow filtration (TFF) are two different methods for separating and purifying biomolecules from a solution.
In normal flow filtration, the solution flows perpendicular to the surface of a filter, and the molecules are retained on the surface of the filter while the permeate passes through the filter. This technique is used for small-scale separations and is relatively simple and cost-effective.
In contrast, tangential flow filtration involves the flow of the solution tangentially across the surface of the membrane, allowing for the separation of larger molecules such as proteins, DNA, and viruses. TFF allows for higher recovery and higher purity of the desired molecules compared to NFF. TFF is commonly used in large-scale separations, particularly in biopharmaceutical production, due to its efficiency and scalability.
Overall, the main difference between NFF and TFF is the direction of the flow and the mechanism of separation, with TFF being a more efficient and effective method for larger-scale separations.
In downstream processing, tangential flow filtration (TFF) is a widely used technique for the separation, concentration, and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, DNA, and viruses from a solution. TFF is particularly useful for large-scale separation of these molecules in biopharmaceutical production.
In TFF, the solution containing the biomolecules flows across a semi-permeable membrane, with the permeate passing through the membrane and the concentrated solution or retentate being recirculated. TFF can be used for various stages of downstream processing, including clarification, concentration, and polishing.
During the clarification stage, TFF is used to remove impurities such as cells, debris, and aggregates from the solution. During the concentration stage, TFF is used to concentrate the desired biomolecule in the retentate, while removing smaller molecules and impurities in the permeate. In the polishing stage, TFF can be used to further purify the biomolecule by removing any remaining impurities or contaminants.
Overall, TFF is a valuable tool in downstream processing as it allows for efficient and scalable separation of biomolecules, providing high recovery and purity of the desired product.
Tangential flow filtration (TFF) is a widely used technique in biopharmaceutical applications for the separation and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, DNA, and viruses. TFF is a key part of downstream processing, which is the process of purifying and isolating a biologic drug after it has been produced in a bioreactor.
TFF is particularly useful in large-scale biopharmaceutical production as it allows for the efficient separation and concentration of the desired biomolecule. TFF can be used for various stages of downstream processing, including clarification, concentration, and polishing.
During clarification, TFF is used to remove impurities such as cells, debris, and aggregates from the solution. During concentration, TFF is used to concentrate the desired biomolecule in the retentate while removing smaller molecules and impurities in the permeate. In the polishing stage, TFF can be used to further purify the biomolecule by removing any remaining impurities or contaminants.
TFF is also used in the development of gene therapies, which involve the delivery of genetic material into a patient’s cells to treat or cure a disease. TFF can be used to purify viral vectors, which are commonly used in gene therapy, by separating the vector from impurities and contaminants.
Overall, TFF is a critical tool in biopharmaceutical production and gene therapy development, allowing for efficient and scalable separation and purification of biomolecules.

